Spin, Planck s constant h and constant G
Let us turn to the theory of electroweak interaction . In the theory of electroweak interaction, the photon J and the boson Z° are a superposition of two other particles - B° and W° :
Z° = W° x cos Q_W - B° x sin Q_W ,
J = W° x sin Q_W + B° x cos Q_W ,
where Q_W is the electroweak Weisberg angle . For 2004, the best estimate of this value is
sin^2 Q_W =0.23120±0.00015 (at Q = 91.2 GeV/sec, as part of a modified minimum subtraction scheme). In an experiment to study the asymmetry of Mellerian scattering at Q = 16 GeV/sec, the value sin^2 Q_W = 0.2397±0.00013 was found to be significantly different from the above value obtained at high energies, and it allows us to establish the dependence of the Weisberg angle on energy. From these data, it can be seen that the Weisberg angle will have a value from 28°10' to 29°15'.
If the Weisberg angle QW is multiplied by 2П, then the angle value is close to 180 degrees. That is, the angle of rotation of the Weisberg when rotating by 2П (360 degrees) it will be about 180 degrees. In order for the Weisberg angle to make a full 360 degree rotation, it is necessary to make a 4П (720 degree) rotation. The ratio of the total rotation by the Weisberg angle to 720 degrees will be 1/2 . This ratio is typical for electrons, neutrons, and other leptons and quarks. It's their back. For ±W and Z bosons, the Weisberg angle doubles because they have a direction of rotation in both directions relative to the isotopic spin. That is, when rotating by 2П ( 360°), the angle of rotation of the Weisberg angle will be 360°. The ratio of the total rotation by the Weisberg angle to 360° will be 1. This is their spin.
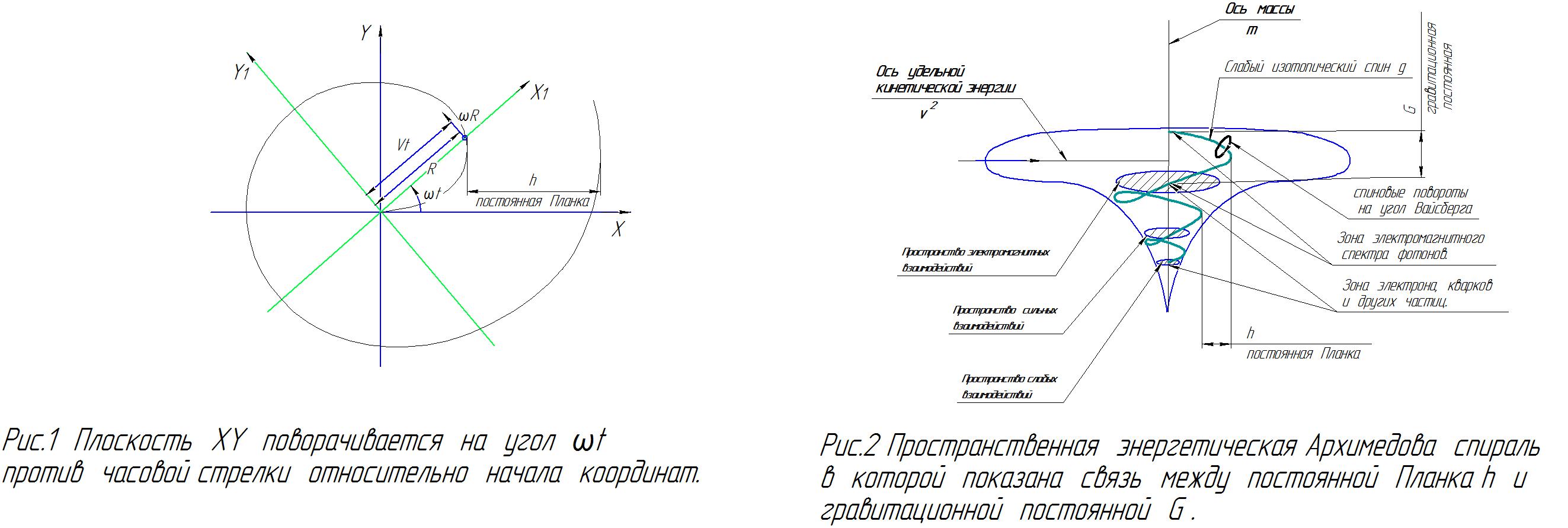
Let us now consider some interesting coincidences between the above formula, which in the theory of electroweak interaction describes the photon ; and the boson Z° as a superposition of two other particles B° and W°, and the formula for the velocity of a point that moves in a Cartesian coordinate system with a constant velocity V, directed parallel to the X axis relative to the plane, in the plane X_1 Y_1, if the plane X_1 Y_1 rotates at a constant angular velocity around the Z axis. In this case, the velocity can be written using the formula :
| V_o| = (V^2 + w^2 x (V x t)^2 )^0,5
The velocity projection V on the X and Y axes will be equal :
V_x = V x cos w x t - ( w x ( V x t ) x sin w x t ;
V_y = V x sin w x t + ( w x ( V x t ) x cos w x t
The motion of the point described by these formulas is shown in Fig. 1.
It is possible to notice the coincidence of formulas for particles in a single space of electroweak interactions and formulas for the velocity of a point in a flat two-dimensional Archimedean spiral in their structural component. That is, the photon J and the boson Z° could be considered as projections on two orthogonal axes . During the existence of the unified space of electroweak interactions, the dimension of the existence of particles was one dimension less and was described by an equation similar to the equation describing the motion of the material point of the Archimedean spiral. The dimension of the existence of particles was described by a two-dimensional energy space. Later, the electroweak energy space was split into the space of electromagnetic interactions, the space of weak interactions and the space of strong interactions, and the energy space became three-dimensional. The relationship between the spaces of electromagnetic, weak, and strong interactions most likely took the form of an Archimedean spatial spiral with transitions between electromagnetic, strong, and weak spaces.
With a change in the dimension of the energy space, the flat energy Archimedean spiral acquired the appearance of a more general case of an energy spatial Archimedean spiral. At the same time appeared ( 3+1+1 ) dimensional space. Three coordinates of this space make up the energy coordinates, one coordinate is the gravitational coordinate, and one coordinate is the time coordinate.
The three energy coordinates of the electromagnetic interaction space of this spiral constitute the lowest energy level. Each coordinate of this space represents a plane orthogonal to other coordinates -planes. So one of these orthogonal coordinate planes corresponds to the magnetic field inductance B, the second coordinate plane corresponds to the magnetic field strength H, and the third coordinate is the electric field strength plane E. The space of electromagnetic interactions is the four-dimensional energy space closest to us. At the same time, the transition from the four-dimensional space of existence of particles in their energy space to our three-dimensional space has characteristics that are associated with Planck's constant h and the gravitational constant G. In addition to the space of electromagnetic interaction with the three plane coordinates mentioned above, there is also a space of strong interactions with three plane coordinates: the baryon number, charm, and truth. There is also a space of weak interactions with three coordinate planes: the lepton number, strangeness, and charm. A spatial energy spiral with transitions between electromagnetic, strong and weak interactions is shown in Fig. 2. When you rotate 360° in this energy spiral, the properties of the space in the energy spiral change. These are different properties of the energy Archimedean spiral and have the properties of spaces of electromagnetic, strong and weak interactions. We can say that spin is a consequence of the transition of the properties of the four-dimensional space of existence of particles with a large number of degrees of freedom into our three-dimensional space with fewer degrees of freedom. Let me remind you that in four-dimensional space, rotation is determined by six angular parameters and four spatial coordinates. In three-dimensional space, rotation is determined by three angular parameters and three spatial coordinates. Therefore, the spins of the particles have the form of spirals of the left or right direction of rotation. In the four-dimensional space of particle existence, spin has the form of a coiled Mobius filament with an angle of rotation by the Weisberg angle . The value of Planck's constant h corresponds to the step of the last turn of the spiral "a" in it in the horizontal direction when exiting four-dimensional space into our three-dimensional space. The value of the gravitational constant G corresponds to the step of the last spiral turn in it in the vertical direction when exiting four-dimensional space into our three-dimensional space. ( Shown in Figure 2 ).
In this regard, ±W bosons and Z bosons are the result of the decay of unstable particles of a higher energy level to particles of a lower energy level. In this case, energy is released in the form of ± W boson or Z boson . In this case, the energy transition occurs along a turn of the energy Archimedean spiral, and as a result, ±W bosons decay into an electron and an antineutrino or a positron and a neutrino at the lowest energy level of ± W boson. At the lowest energy level, the Z boson decays into quark–antiquark forming mesons. ± W bosons correspond to the transition along the spiral of the energy spiral, when the sum of the turns of the spiral direction ( left or right spiral ) plus, the direction of rotation at the Weisberg angle has one direction. In this case, the left direction corresponds to the -W boson, and the right direction corresponds to the +W boson. During the transition along the energy turn of the Archimedean spiral, when the sum of the turns of the spiral direction ( left or right spiral ) plus the direction of rotation by the Weisberg angle have a different direction . As a result, the electric charge of the Z boson is zero.
Свидетельство о публикации №222101500935